What are the Load Balancing Policies supported in the EdgeADC?
A load-balancing policy is a set of rules or algorithms determining how incoming network traffic will be distributed across multiple servers. This is crucial for ensuring that no single server becomes a bottleneck, leading to improved application responsiveness and availability. Load balancing policies play a vital role in managing the workload on a network, especially in environments with varying traffic patterns or situations where high availability is critical.
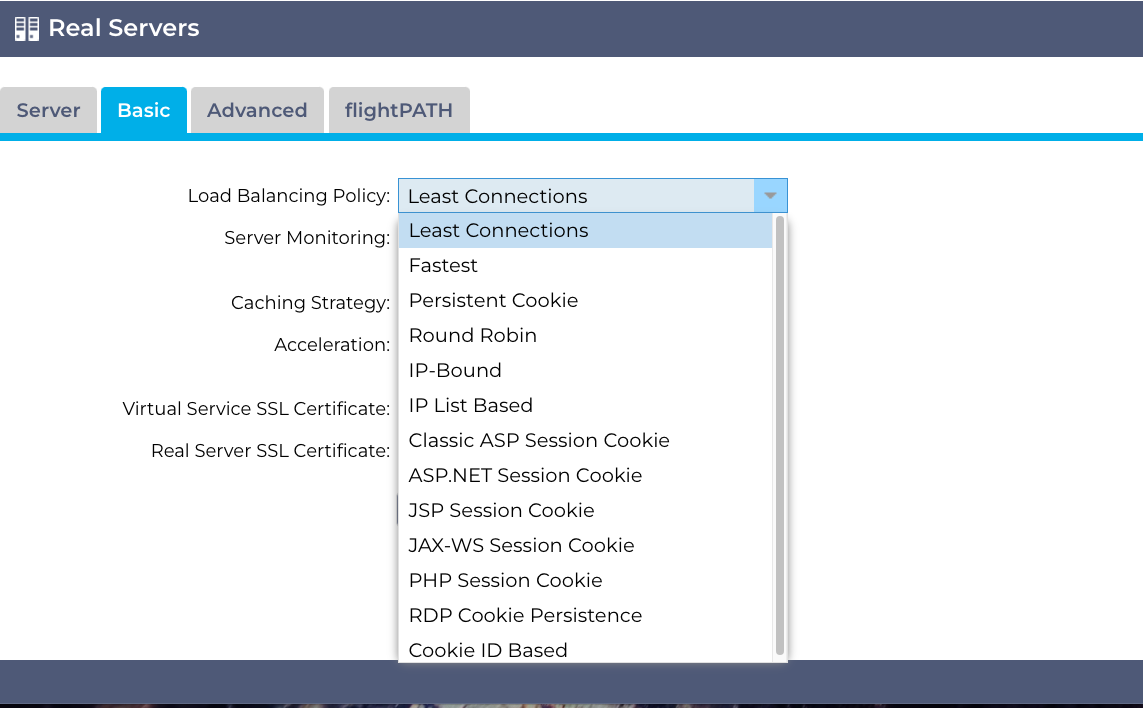
The load-balancing policies supported in the EdgeADC are:
| Option | Description |
| Least Connections | The load balancer will keep track of the number of current connections to each Real Server. The Real Server with the least number of connections receives the subsequent new request. |
| Fastest | The Fastest load balancing policy automatically calculates the response time for all requests per server smoothed over time. The Calculated Weight column contains the automatically calculated value. Manual entry is only possible when using this load balancing policy. |
| Persistent Cookie | Layer 7 Session Affinity/Persistence The IP list-based load balancing mode is used for each first request. The ADC inserts a cookie into the headers of the first HTTP response. After that, the ADC uses the client cookie to route traffic to the same back-end server. This cookie is used for persistence when the client must go to the same back-end server each time. The cookie will expire after 2 hours, and the connection will be load balanced according to an IP List Based algorithm. This expiry time is configurable using a jetPACK. |
| Round Robin | Round Robin is commonly used in firewalls and basic load balancers and is the simplest method. Each Real Server receives a new request in sequence. This method is only proper when you need to load balance requests to servers evenly; an example would be look-up web servers. However, when you need to load balance based on application load or the server load, or even ensure that you use the same server for the session, the Round Robin method is inappropriate. |
| IP Bound | Layer 3 Session Affinity/Persistence Cookie. In this mode, the client’s IP address forms the basis to select which Real Server will receive the request. This action provides persistence. HTTP and Layer 4 protocols can use this mode. This method is helpful for internal networks where the network topology is known, and you can be confident that there are no “super proxies” upstream. With Layer 4 and proxies, all the requests can look as if they are coming from one client, and as such, the load would not be even. With HTTP, the header (X-Forwarder—For) information is used when present to cope with proxies. |
| IP List Based | The connection to the Real Server initiates using “Least connections” then, session affinity is achieved based on the client’s IP address. A list is maintained for 2 hours by default, but this can be changed using a jetPACK. |
| Shared IP List Based | This service type is only available when the Connectivity Mode is set to Direct Server Return. It has been primarily added for support with VMware load balancing. |
| Persistent Cookie | Layer 7 Session Affinity/Persistence The IP list-based load balancing mode is used for each first request. The ADC inserts a cookie into the headers of the first HTTP response. After that, the ADC uses the client cookie to route traffic to the same back-end server. This cookie is used for persistence when the client must go to the same back-end server each time. The cookie will expire after 2 hours, and the connection will be load balanced according to an IP List Based algorithm. This expiry time is configurable using a jetPACK. |
| Classic ASP Session Cookie | Active Server Pages (ASP) is a Microsoft server-side technology. With this option selected, the ADC will maintain session persistence to the same server if an ASP cookie is detected and found in its known cookies list. On detection of a new ASP cookie, it will be load balanced using the Least Connections algorithm. |
| ASP.NET Session Cookie | This mode applies to ASP.net. With this mode selected, the ADC will maintain session persistence to the same server if an ASP.NET cookie is detected and found in its list of known cookies. On detection of a new ASP cookie, it will be load balanced using the Least Connections algorithm. |
| JSP Session Cookie | Java Server Pages (JSP) is an Oracle server-side technology. With this mode selected, the ADC will maintain session persistence to the same server if a JSP cookie is detected and found in its known cookies list. On detection of a new JSP cookie, it will be load balanced using the Least Connections algorithm. |
| JAX-WS Session Cookie | Java web services (JAX-WS) is an Oracle server-side technology. With this mode selected, the ADC will maintain session persistence to the same server if a JAX-WS cookie is detected and found in its list of known cookies. On detection of a new JAX-WS cookie, it will load balanced using the Least Connections algorithm. |
| PHP Session Cookie | Personal Home Page (PHP) is an open-source server-side technology. With this mode selected, the ADC will maintain session persistence to the same server when a PHP cookie is detected. |
| RDP Cookie Persistence | This load balancing method uses the Microsoft-created RDP Cookie based on username/domain to provide persistence to a server. The advantage of this method means maintaining a connection to a server is possible even if the IP address of the client changes. |
| Cookie-ID Based | A new method very much like “PhpCookieBased” and other load-balancing methods, but using CookieIDBased and cookie RegEx h=[^;]+
This method will use the value set in the Real Server’s notes field “ID=X;” as the cookie value to identify the server. This, therefore, means it is a similar methodology as CookieListBased but uses a different cookie name and stores a unique cookie value, not the scrambled IP, but the ID from the Real Server (read in at load-time.) The Default value is CookieIDName=”h”; however, if there is an override value in the virtual server’s advanced settings configuration, use this instead. NOTE: We overwrite the cookie expression above to replace h= with the new value if this value is set. The last bit is that if an unknown cookie value arrives and matches one of the Real Server IDs, it should select that server; otherwise, use the next method (delegate.) |
